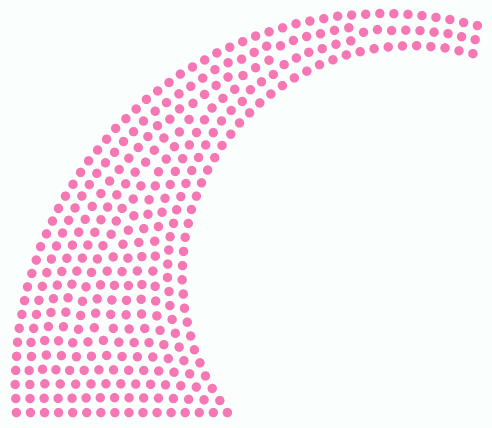
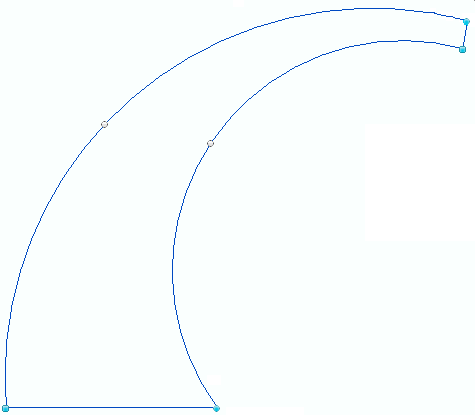
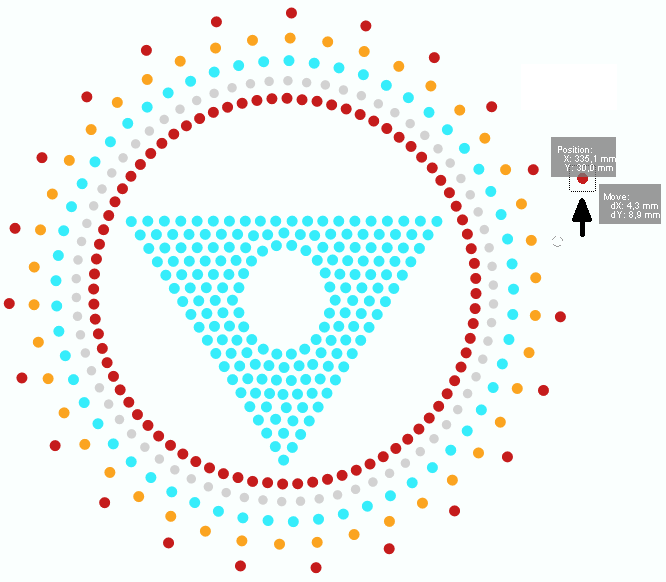
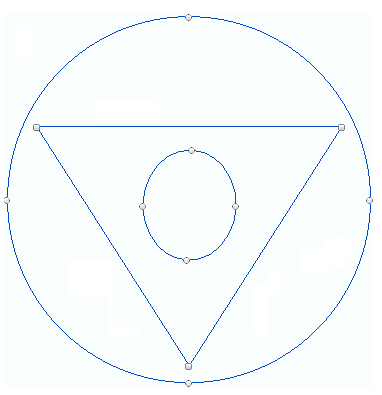
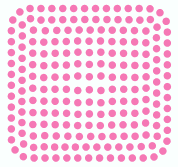
A bling design is a file that contains a set of data that define the design made with hotfix rhinestones and/or sequins/spangles, which is ready for the production of rhinestones/sequins/spangle transfers (by hand, through cutters or cnc-machines, or through automatic motif making machines).
There are 2 kind of bling design files:
•Bling machine design files, also known as expanded designs
•System native design files, also known as condensed designs
It is very easy (and absolutely necessary) to understand why both kind of files exist, and to decide when to use each of them.
The following table compares the main characteristics of both kind of bling design files:
Bling machine files (expanded designs) |
System native files (condensed designs) |
|---|---|
|
|
•Machine design files are compatible with different kind of production machines. They are designs ready to use or produce with machines. |
•Production machines cannot read system design files, but the software can easily convert it to machine specific file format while exporting it. |
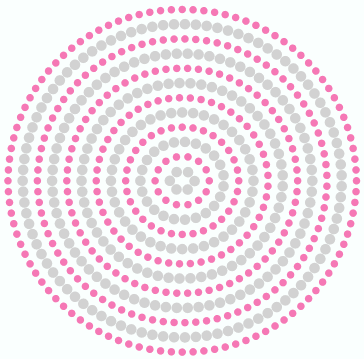
•BEADS ORIENTED Machine design files contain (at least) the information about each bead type and beads position (expanded data). Then machine design files are also known as expanded designs. |
•OBJECT ORIENTED System design files are the native files used by the software to store the complete design specification (it is much more more than beads types and positions). This is an all in one file format which contain detailed information about all the objects the design is made of (objects and properties, images, settings, beads, etc) to produce the beads types and beads positions. The digitizing applications use system design files to simplify the designs creation and editing. It is also known as native designs or system condensed designs. |
•Regrettably, there is no a unique standard format of bling machine design files for all kind of production machines, as many machine manufacturers have developed their own proprietary design file format to load the designs into the machine (see machine specifications). Depending on the machine model, designs can be sent to the production machines from USB memory or direct connection from a computer. There is a list of the compatible production equipment in the bling compatibility chapter. |
•Each software manufacturer has created its own proprietary system file format. Our system (native) format has the extension “DSG”. After a design is created and stored as a condensed design, it can be converted and exported in a single step for the specific production machine for production. |
Expanded designs / Bling machine files
|
As mentioned, expanded designs contain the data required by the production machine. All the machine file formats contain 2 basic elements: beads types and beads positions. Some machine file formats may include complimentary information.
|
Then, expanded designs is basically a sequence of:
•Beads Types |
Types refer to the decoration type (rhinestone, nailhead, sequin, spangle, etc), the shape, the size and the color. |
•Beads Positions |
Positions refer to the location of each individual bead. |
Condensed designs
|
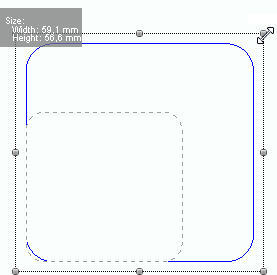
Certainly, a designer could create designs by inserting each individual bead type on the corresponding position (old method to create hotfix designs many years ago). Today, a designer can define a rectangle with only 4 points, and the digitizing applications can automatically generate the beads to cover all that shape according to pre-defined characteristics. As that rectangle created with 4 points or any other more complex geometric shape created with more points can be turned into many beads, we say that it is a condensed design. The conversion from condensed designs to expanded designs is named beads generation. |
The basic elements of the condensed designs are the objects (or hotfix objects). Objects are defined by:
•Geometry |
That is basically the shape. The geometry includes the nodes (the points that define the shape) and some complementary elements. |
•Properties |
That is basically the bling fill style. The properties include the main fill style and other parameters to adjust the final beads types and positions. |
There are many types of objects grouped in categories (see later).
Advantages of working with condensed designs over expanded designs
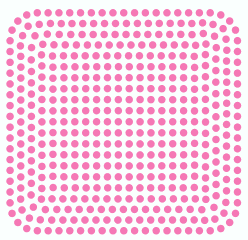
To understand one of the many advantages of the condensed designs compared to expanded designs, compare the process to scale a simple design in both cases:
Using condensed design you can scale any object of the design (or the whole design) just re-sizing the rectangle that contains that object. The beads are automatically re-created by the digitizing application keeping the original density.
|
|
|
original object |
resize object |
re-calculated object |
Instead, scaling the expanded design would be a very difficult task, almost impossible, as it will require to insert and move many beads to get the scaled design (a simple scaling won't keep the beads density).
In addition, if you want to change the fill style of any object or if you want to change any other property (like the density, etc) it is easy and immediate on condensed objects, while it is not possible to change those characteristics on expanded designs.
As a conclusion,
It is more convenient for designers to create and store the designs as condensed designs (system format) and convert or export to expanded designs for any production machine file format when the design is required for the production.
See some examples of object types (condensed) with the corresponding beads (expanded).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|